| Home Page
Contact Page
Favorite Links
Locomotion and General Structure
Natural Habitat
Reproduction
Endocystosis
Taxonomy and Lab Observations
|
|
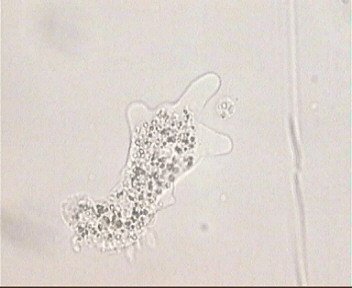
Endocytosis is the process by which amoebas take in ("eat") substances. Endocytosis is divided into two processes: phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Phagocytosis is the most common way amoebas and other protozoans obtain their food. It is the engulfing and digesting of microspically visible particles. On the other hand, pinocytosis is the engulfing and digesting of dissolved particles. It sometimes refered to as "cell drinking". Endocytosis occurs when a portion of the cell cytoplasm moves forward and surrounds the particle that has come in contact with the cell membrane. The movement of the cytoplasm continues until the particle is completely engulfed in a pocket called a "vesicle". The vesicle then moves towards the body of the cell where it meets and fuses with a lysosome (responsible for the digestion of the particle). The useful compounds are absorbed and the useless ones are taken out of the cell's body. The picture in the right side shows an amoeba about to engulf a food particle |
 |
|
Phagocytosis caught in video!
Click here! |
|
|